Point Cloud > ProcPlane > From points 
With this function, several points of the point cloud are selected for the generation of the processing plane in such a way that a plane can be found which is as close as possible to the object to be processed, for example a wall.
The plane determined by the choice of points can also be parallel or perpendicular to another plane or an axis. In this way, for example, it is also possible to realize the case, which is usually required in practice, that a plane should be as close as possible to the object to be machined, but should still be perpendicular to the XZ-plane or parallel to the Z-axis of the world coordinate system.
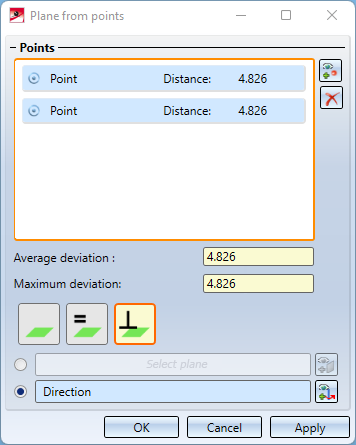
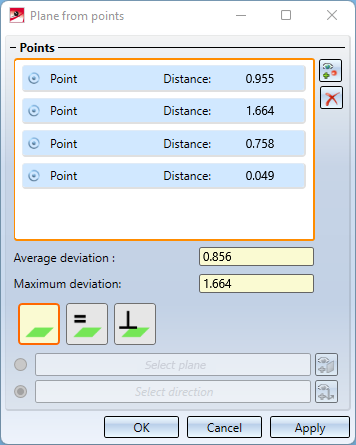
- List of selected points
-
Display of average and maximum deviation of points from the plane
- Mode for alignment of the new processing plane
- Selection of a reference plane or direction - only in the modes Parallel and Orthogonal
- Acceptance of the processing plane displayed in the preview
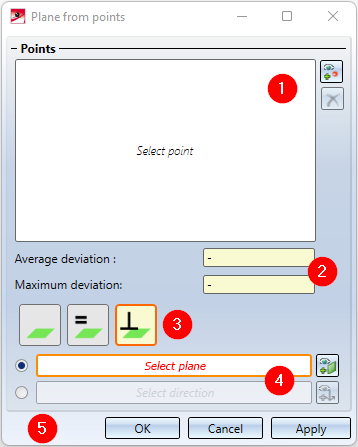
To select the points for the plane, call the function. The Select point  option is active in the Free
option is active in the Free  mode and the selected points are added to the list. If you want to remove a point from the list, select the corresponding entry, right-click and select Remove elements from list
mode and the selected points are added to the list. If you want to remove a point from the list, select the corresponding entry, right-click and select Remove elements from list  . If you want to delete the entire selection list, click the
. If you want to delete the entire selection list, click the  icon to the right of the selection list.
icon to the right of the selection list.
As soon as you have selected more than three points, not all points have to lie exactly on the averaged plane. The Maximum deviation is the largest distance that one of the selected points in the list has to the plane. The average deviation is the averaged value, i.e. the sum of all distances of the points divided by the number of points.
The following options are available for aligning the plane:
|
|
Free |
Here you define the plane by freely selecting points. As soon as you have selected three points, the plane is displayed. By selecting further points you change the position of the plane, since the distance to each other is recalculated after each further point.
|
|
|
Parallel |
In this mode you first select - after activating the corresponding radio button - the direction (axis) or the plane to which the new processing plane is to be parallel. The selection of the direction is preset. To determine the direction or the plane, the usual HiCAD functions for selecting the plane or the axis are available in the context menus (right-click).
In addition, you also have the possibility to click the direction or the plane directly in the preview of the coordinate system.
To change the direction or the plane, click on the After selecting the direction or the plane, select at least 2 points for the new processing plane. Then the average distance of the points to the new processing plane is determined and the plane is displayed in the preview.
|
|
|
Orthogonal |
In this mode you first select - after activating the corresponding radio button - the direction (axis) or the plane to which the new machining plane is to be perpendicular. The selection of the direction is preset. To determine the direction or the plane, the usual HiCAD functions for selecting the plane or the axis are available in the context menus (right-click). In addition, you also have the option of clicking the direction or the plane directly in the preview of the coordinate system.
|
|
The only reliable criterion when processing point clouds is the Z direction of the world coordinate system. Therefore, in most cases, a processing plane is required when constructing a point cloud, which fits the object as well as possible, but does not have an angle - even if the point cloud itself has an angle, e.g. due to inaccuracies. In this case, such a processing plane can be realized as follows:
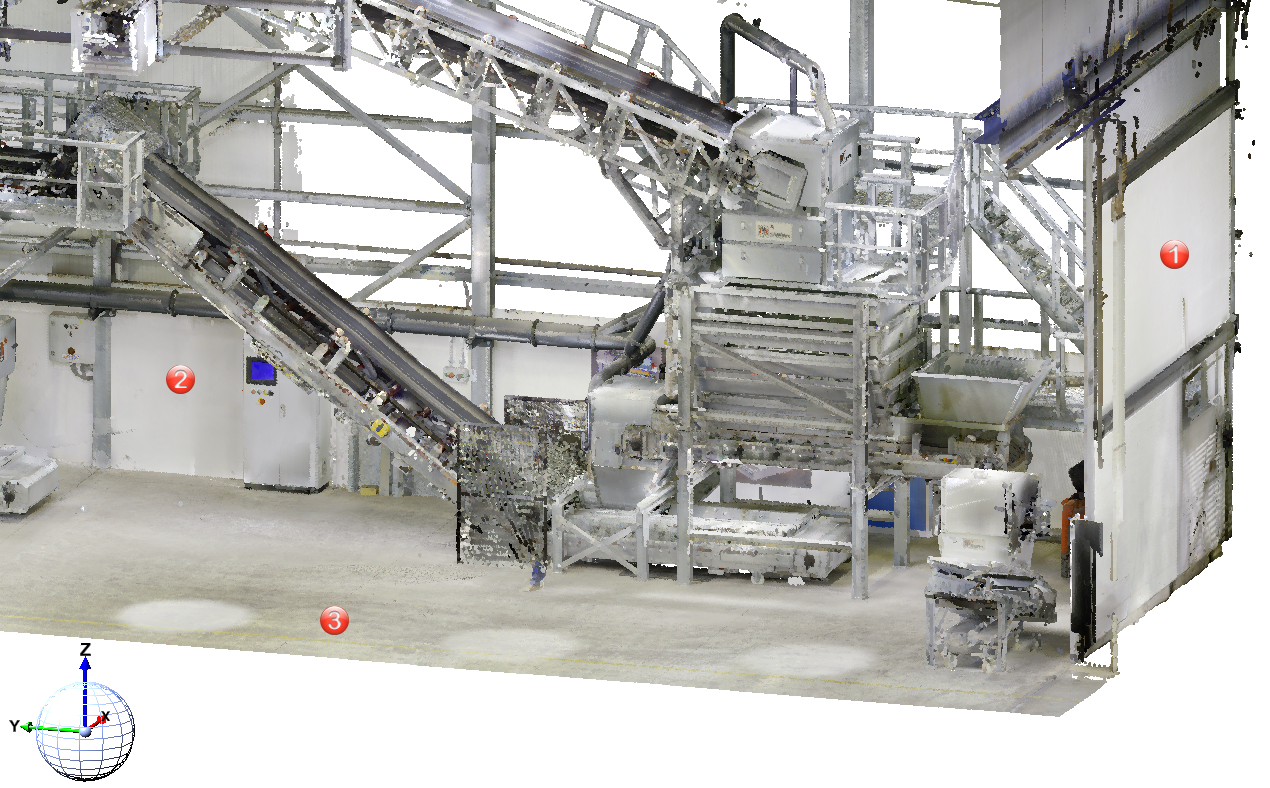
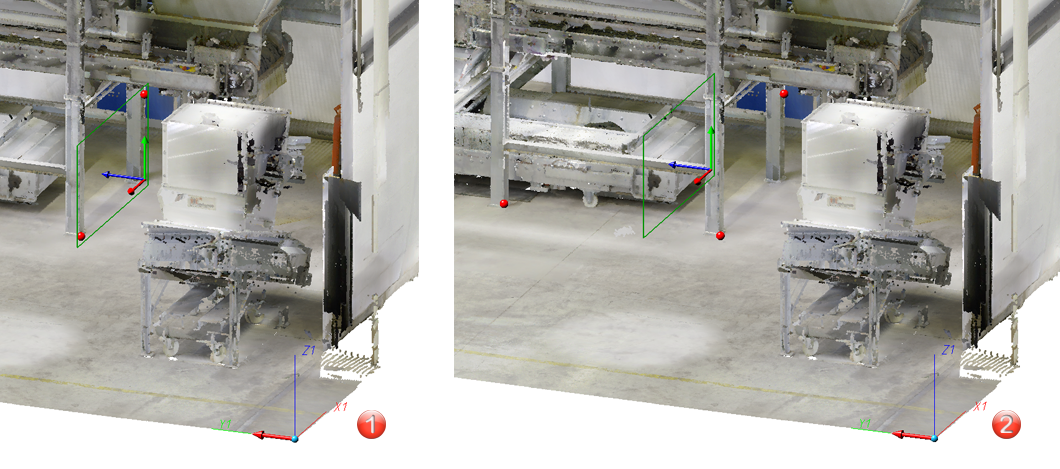
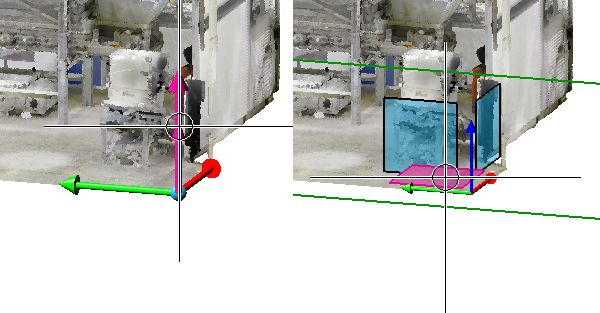
Example: Let us assume that you want to attach further elements at the points (1), (2), and (3). The World CS is active.
Then you will select the processing planes as follows: (1) Mode: Parallel, Plane: XZ-plane (2) Mode: Parallel, Direction: Z-axis (3) Mode: Orthogonal, Direction: Z-axis |
Once you have entered all the required data, selecting Apply or pressing the middle mouse button will apply the layer - as shown in the preview. In contrast to OK, the dialog window remains open. This allows you to create additional layers directly.
|
When determining further points for the new processing plane, the position changes. The position of the plane results from the averaged points.
(1) Direction (X-axis) and 2 points, (2) Direction and 2 points identical with (1) plus third point |

Working with Point Clouds - Procedure • Point Cloud Functions • Working with Point Clouds - An Example

 or the.
or the.  symbol, respectively.
symbol, respectively.