Plant Engineering > Pipeline Tools > Change  > Change route
> Change route 
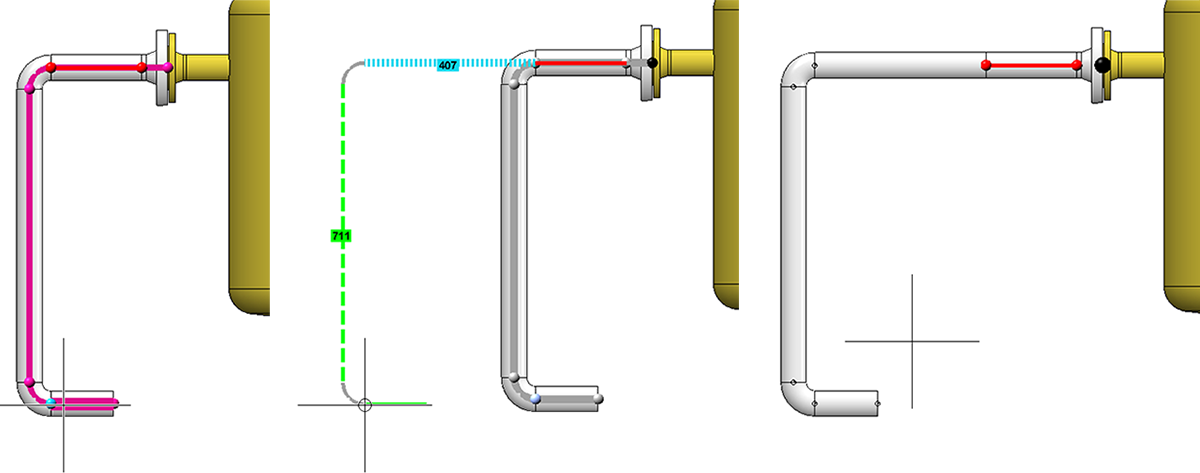
A route change also allows the creation of new straight sections. For this the Create straight sections checkbox must be active. A typical use case is the increase of the distance between two parts, such as the illustrated elbow and the flange.
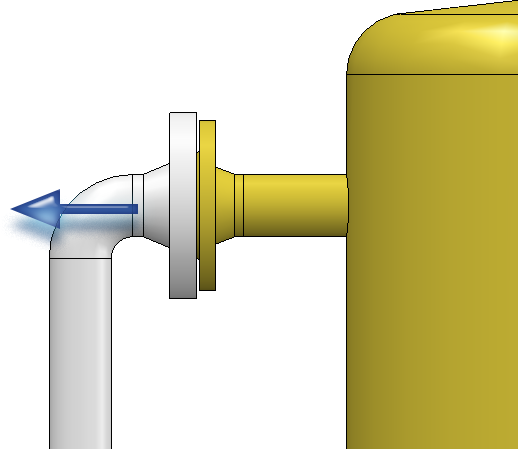
At this point you can reach your target as follows:
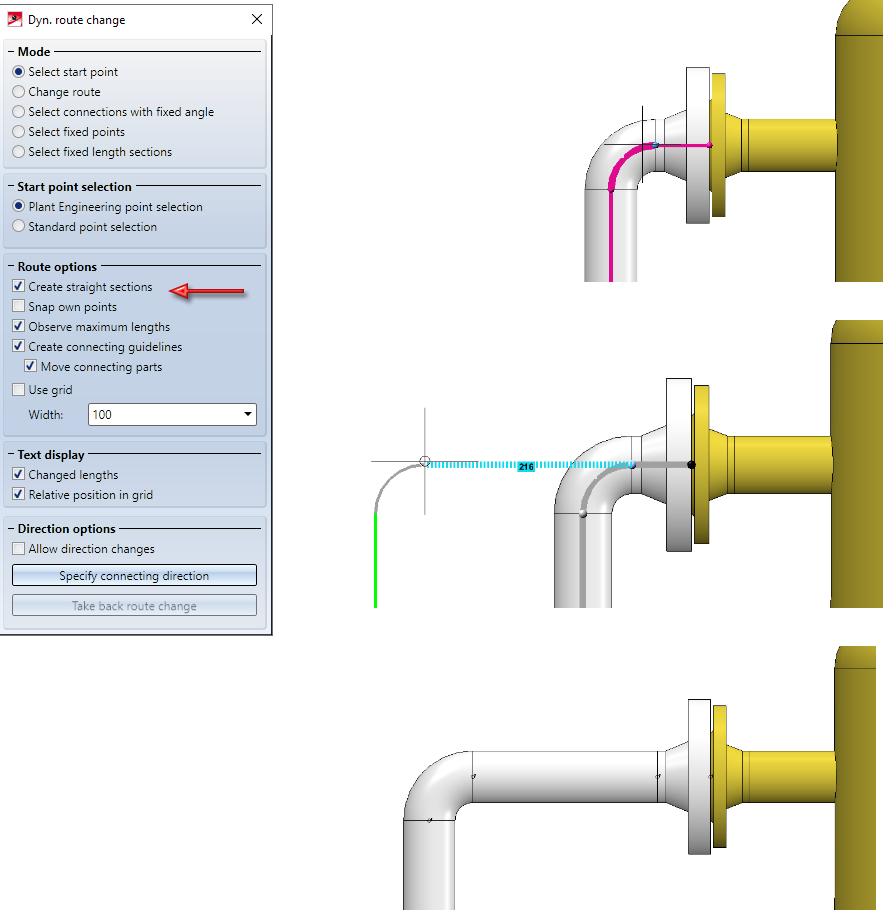
Simply pull the elbow away from the flange. A piece of straight pipe appears between the elbow and the flange. Please note that it is important to know on which side of a connection the cursor is located when selecting the connection.
We select the connection at the elbow once more. Note the different results depending on which side the connection is selected from.
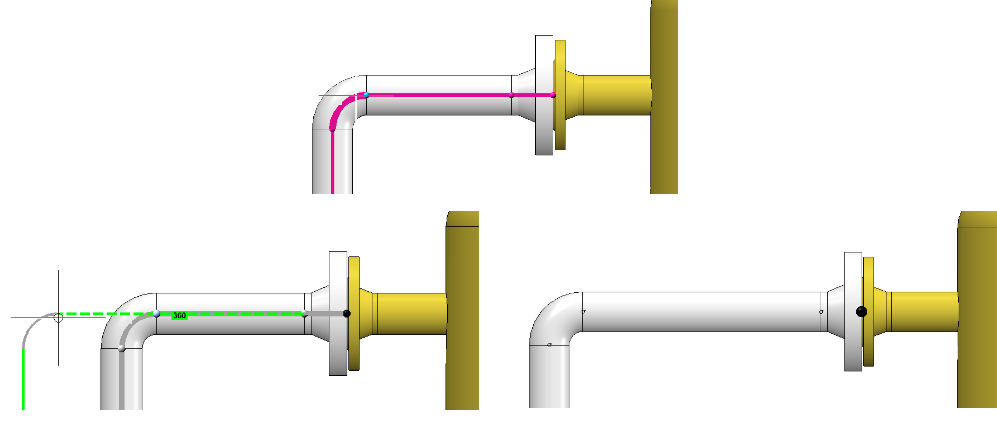
Elbow side
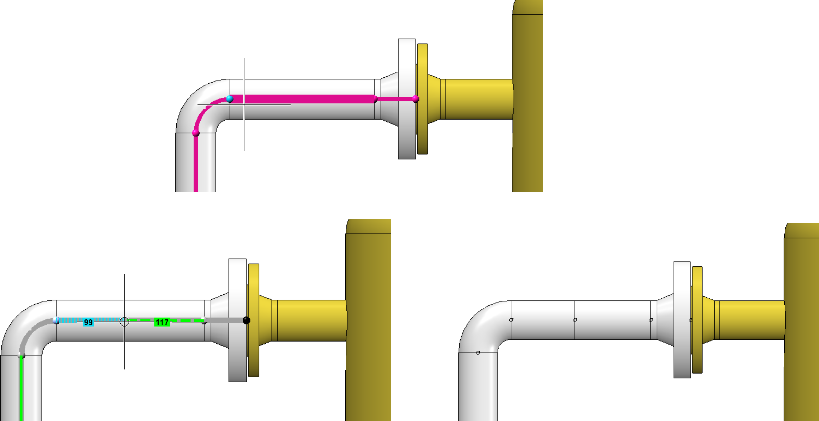
Pipe side
If you pull the elbow again, the previously created straight pipe will be extended. If, on the other hand, you drag the straight pipe, a new straight section is created between the straight pipe and the elbow.
In general, dragging on a connection causes a new straight section to be created. Unless a straight pipe follows which may be changed in its length. Then its length is increased until its maximum length is reached. From then on a new straight section is created. If you had fixed the length of this straight pipe, the behaviour would be the same as that of a straight pipe whose maximum length has been reached, i.e:
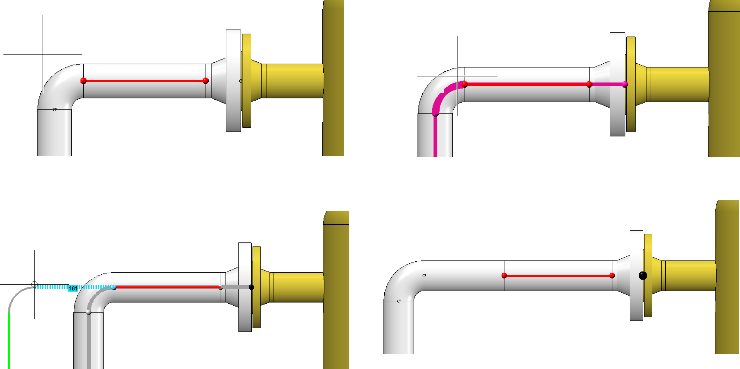
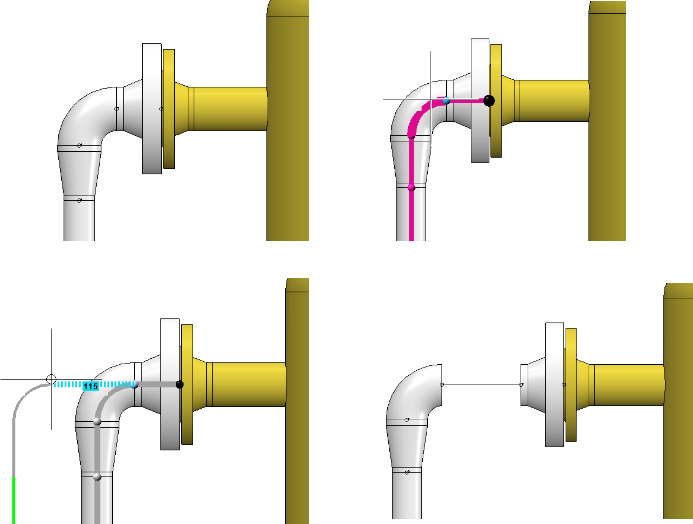
If you push a connection, no new straight sections are created there. However, a new straight section can be created at another location if the target position would otherwise not be reachable, which was forced by the length-fixed section in the following:
The newly created straight pipe is created as a modified copy of an already existing straight pipe. The existing straight pipes within the same pipeline are used to determine the straight pipe to be copied. If one is found that matches the connection conditions, a length-adjusted copy of this pipe is installed. If such a pipe is not found, a leading edge pull section is inserted instead. In the following example a straight pipe with a nominal diameter of 50 is required, but after the reduction only pipes with a nominal diameter of 32 follow:
|
Limitations:
|