Transform Surfaces
3-D Standard > Tools > Surface
The functions of this menu enable you to transform surfaces by moving, rotating, mirroring or scaling them, with a distinction being made between:
- Retain surrounding surfaces (Retain direction)
Only the surface boundaries are adapted.
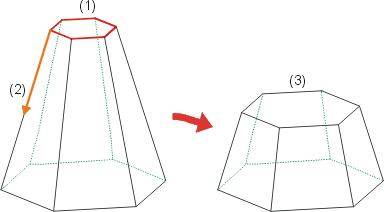
(1) Surface, (2) Displacement vector, (3) Adjustment of the surface boundaries
- Retain facet boundary (constant surfaces)
Neighbouring surfaces are adapted by means of inclination or triangulation.
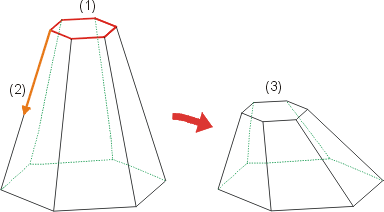
(1) Surface, (2) Displacement vector, (3) Adjustment of the neighbouring surfaces by means of inclination
| Retain surrounding surfaces | Retain facet boundaries | |
|
|

|
Move (direct) Moves the surface by specifying two points |
|
|
Move surface, with vector Moves the surface by specifying a displacement vector |
|
|
|

|
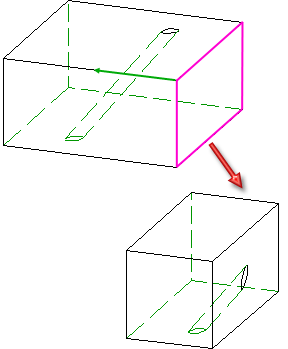
Rotate, about edge/2 points Rotates the surface by specifying edge + points |
|
|
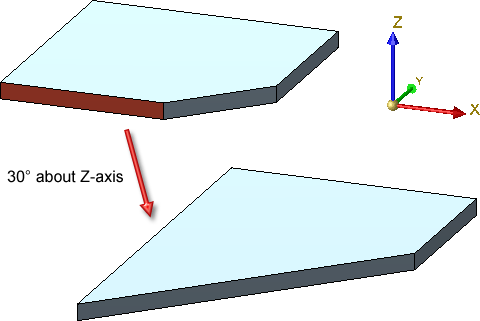
Rotate about axis Rotates the surface about an axis |
|
|
|
|
Move+Rotate Moves and the surface simultaneously |
|
|

|
Similarity transformation Moves, rotates and scales the surface |
|
|

|
Scale Scales the active object or changes volume, mass or surface area |
|
|

|
Last transformation Applies the transformation that was last applied to a surface to the selected surface |
|
|

|
Changes surface radiuses of analytical cylinders or polyhedral cylinders by specifying the new value |
|
|

|
Change surface radius, via point Changes surface radiuses of analytical cylinders or polyhedral cylinders by specifying a point on the lateral surface. |
|
|
Reduces/enlarges circular or polyhedral surfaces by specifying the new value |
|
|
|
Change edge radius, via point* Reduces/enlarges circular or polyhedral surfaces by specifying a point on the medial surface |
* These functions are only available for Transform surfaces, Retain surrounding surfaces.
Clicking the arrow  below Surface icon opens a pull-down menu with further surface functions.
below Surface icon opens a pull-down menu with further surface functions.
![]() Please note:
Please note:
- The functions work in a similar way to the corresponding Transformation functions for parts.
- The Surface
selection menu is automatically displayed for selection of the surfaces
to be transformed. However, this is only the case if the
 Always display window option was active when
you last exited the Surface Selection menu.
Once you have called the function, you can also use the right mouse button
to activate the Surface menu.
Always display window option was active when
you last exited the Surface Selection menu.
Once you have called the function, you can also use the right mouse button
to activate the Surface menu. - You can also use the cursor to move surfaces dynamically. Simply enter 0 instead of the length of the displacement vector.
- When moving or rotating surfaces, changing topologies will be considered. These functions can also be applied to freeform surfaces.

Surface Selection Menu (3-D) • Change Radiuses (3-D) • Transform and Clone Part (3-D)