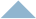
Fillet Options
3-D Standard > Process > Fillet 
You define the fillet parameters via the checkboxes, option fields and input fields of the Radius dialogue window.
- Radius
- Constant filleting
- Variable filleting - linear or tangential
- Continue with tangential edge
- Transitions
Radius
Enter the fillet radius in the input field.
This radius will be used as default value for the subsequently identified edges and surfaces. Of course, you may also change the radius for each of the subsequently identified objects.
Constant filleting
In constant filleting, the fillet is achieved by means of cylinders or torus surfaces. The fillet radius is the same on all points of the edge to be filleted.
To fillet edges constantly, deactivate the Variable checkbox.
Constant fillet
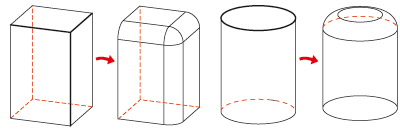
Variable filleting
With variable filleting, you can choose different fillet radii on the start and end points of the selected edges as well as on any other intermediate points. The variable fillet can either be performed linearly or with tangential border connection.
To fillet edges variably, proceed as follows:
- In the Fillet window, activate the Variable checkbox.
- Choose the fillet path - linear or tangential - by activating the relevant option field.
Variable Filleting with different
radii at the start, mid and end points of the edge
Centre: Tangential, Right: Linear
Continue with tangential edge
If, when filleting an edge, you also want all tangentially adjoining edges to be filleted, activate the Continue with tangential edge checkbox. This is possible with both constant and variable filleting.
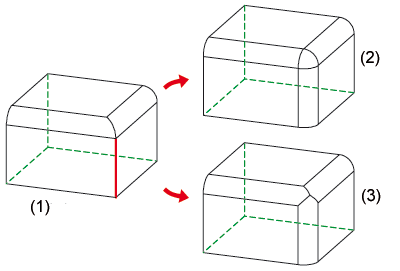
(1) Original part, (2) Fillet with tangential continuation, (3) Fillet without tangential continuation
Transitions
This option enables you to have an influence on the way in which the fillet surface is created:
- Automatic
The fillet algorithm automatically selects the strategy, which can also simultaneously contain elements of the two following strategies. If there are several fillet options, the algorithm decides automatically. - Retain
edge
You can guide the fillet algorithm so that non-tangential edges which the fillet surfaces meet are changed as little as possible. This means, however, that the fillet surfaces need to be divided more frequently. - Retain
fillet surface
If fillet surfaces meet non-tangential edges, this option retains the fillet surface as far as possible, i.e. it does not further subdivide it. This also means, however, that the corresponding non-tangential edges change.
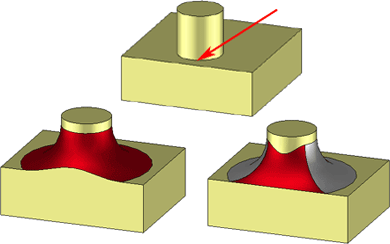
Left: Automatic or retain fillet surface, Right: Retain edge - several fillet surfaces are created