Surface from Curve Mesh
3-D FFS >From c-edges > Surface from curve mesh 
Use this function to create a freeform surface by interpolation of a curve-mesh. The resulting surface is also known as "Gordon surface".
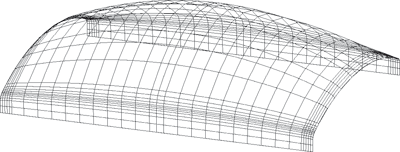
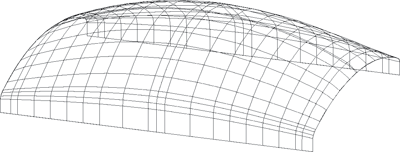
During this procedure, entire curves are interpolated instead of individual points. A surface part of freeform surface is determined by the specification of four boundary curves. The specification of an entire mesh of such boundary curves enables the creation of complex surfaces. The interpolation of the curve mesh is realised via the specification of parameter lines in m- and n- direction. This means that the lines of the curve mesh become parameter lines on the Gordon surface and therefore must not intersect.
At least two mesh lines need to be defined per parameter direction. The mesh line orientation required for the Gordon algorithm is automatically determined by HICAD . If you have closed mesh lines, at least 3 guidelines should be available in the intersecting parameter direction.
The dialogue window Interpolate mesh is displayed, enabling you to specify all required data.
- Specify the horizontal edges, i.e. the parameter lines in n-direction. Activate the Horizontal edges radio button or left-click once in the Horizontal edges option field. Then identify the required edges.
- Specify the vertical edges, e.g. the parameter lines in m-direction. Activate the Vertical edges radio button or left-click once in the Vertical edges option field. Then identify the required edges.
- Specify the name of the new part.
- If you have closed mesh lines you can determine the treatment for base and top surface in the Solid field. Select the required entry from the listbox - Close or Leave open.
- In the Form field, select the procedure for parameterisation:
- Equidistant
The entire topology is taken into account, i.e. each edge is parameterised from 0 to 1. - Curve lengths
The entire c-edge is paremeterised according to the arc length. - Secants
The parameterisation is performed according to start point and end point of secants.
- Click Preview if you want to check the freeform surface before applying it to your drawing.
- Select OK to apply the freeform surface.
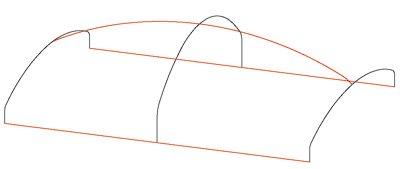
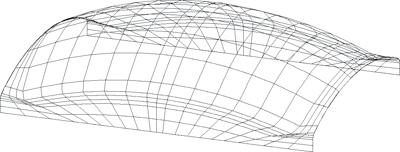
Curve mesh; the horizontal edges are shown in red, the vertical edges in black.
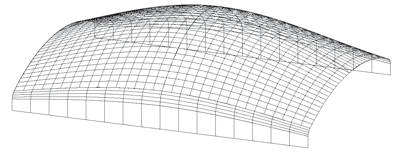
The image below illustrates the difference from freeform surface creation by cross-section interpolation. Here, the created freeform surface runs exactly through the cross-sections.

Interpolate Cross-Section (3-D FFS) • Overview of Functions (3-D-FFS) • Freeform Surfaces