Freeform Surfaces
Today modern product designs have increasingly complex and sophisticated surface structures. Whether household goods, furniture or car bodies, many of these products get their design by arbitrarily curved surfaces defying analytical description. Such surfaces are called Freeform Surfaces. HiCAD provides the appropriate technology for the creation and processing of such surfaces.
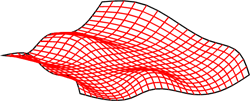
Example of a Freeform Surface

Examples of Freeform Surface-based designs
Special mathematical procedures are used to describe Freeform Surfaces, based on a quantity of control points, with each control point corresponding to a 3-D point. If the calculated freeform surface coincides with these 3-D points, the procedure is called "interpolation". If the surface only gets close to these 3-D points, the procedure is called "approximation". Possible is, for instance, the creation of
- Spline surfaces,
- B-Spline surfaces,
- NURBS (Non-Uniform-Rational-B-Spline-Surface),
- Bezier surfaces or
- Patches.
Freeform surfaces are always generated in the same way:
- Definition of the control points via specification of 3-D points.
This can be done in different ways:
- Arrange c-edges in space. The points of these c-edges represent the control points.
- Detect the control points of a model with a coordinate measuring machine and transfer the data via an interface to HiCAD.
- Take over the VDAFS, respectively VDAIS data.
- Calculation of a 3-D curve, respectively a freeform surface
- via interpolation, in order to create coincidences with predefined points,
- via approximation, in order to create compensating curves from a quantity of experimentally obtained data.
- Freeform surface representation on the screen
Each freeform surface is represented via the calculated points of a curve which are connected by straight lines. The number of points can be preset by the (n,m) parameter values. The greater the number of parameter values, the more precise and detailed will be the representation.
Before generating a freeform surface, create a new drawing or load an existing drawing.
You will find the functions for the generation and processing of freeform surfaces on the 3-D FFS tab. The functions for creation and processing of freeform curves are available via the Sketch tab.
HiCAD offers the following procedures for generation of freeform surfaces:
- The freeform surface is derived from curves, e.g. by moving or rotation of a curve, by placing of cross-sections on a guideline or by projection of a surface onto a plane.
- The freeform surface is created by connecting splines or cross-sections and interpolation of curve meshes.
- Connecting surfaces are created between two arbitrary objects (solids, surfaces or curves) which can then be connected smoothly if required.
- Connected surface parts, so-called "patches", are fitted into predefined boundary curves.
Furthermore, freeform surfaces are also created during filleting of 3-D parts. Internally, a freeform surface is always saved as B-spline surface, respectively a a NURBS, even if it has been created as a cubic spline surface or an Akima spline surface. This is important for the modelling of freeform surfaces, as only B-spline surfaces, respectively NURBS can be modified locally.