Finds the in the current drawing 3-D parts with identical geometry.

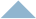
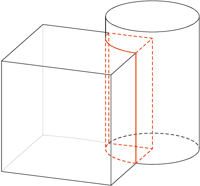
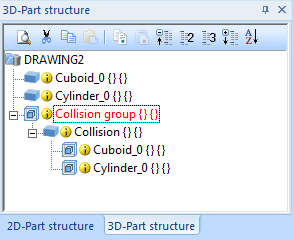
Checks whether parts in the drawing collide with each other.
Clicking  opens a pull-down menu with further collision check functions.
opens a pull-down menu with further collision check functions.

Colour-marks referenced 3-D parts of the drawing.
Clicking  opens a pull-down menu with further functions for the marking of referenced parts.
opens a pull-down menu with further functions for the marking of referenced parts.

Rebuild
Rebuilds surfaces of a part, thus guaranteeing, amongst other things, that the bordering of facets is exactly located on the surface (this is important before performing Boolean operation). This function can also be helpful if one of the other checking options was unsuccessful.
You can choose to recreate the body for the active part or the entire drawing.
Freeform surfaces which can be displayed as analytical surfaces are automatically converted when regenerating the body. If you do not want this to happen, you need to change the entry Should FFS be converted, if possible, into analytical surfaces once they are created?..... from 1 to 0 in the system file SPLINE.DAT.
Clicking  opens a pull-down menu with further functions, e.g. Data structure check. With these functions you can check individual parts or the entire drawing for errors in the part structure.
opens a pull-down menu with further functions, e.g. Data structure check. With these functions you can check individual parts or the entire drawing for errors in the part structure.

Manages user-specific variables.

The Design Checker is a tool that enables you to increase the quality of your drawings and reduce costs and time through an early detection of errors in the design. You can auto-check your drawings for their compliance with specific construction guidelines; it detects, for example, invalid features, incorrect bolting sets, dummy parts, and much more. If any errors are detected, HiCAD issues an appropriate message and suggests corrections.
Clicking  opens a pull-down menu with further data structure check functions.
opens a pull-down menu with further data structure check functions.

Use this function to check whether a cylindrical pin that was inserted for the connection of two parts has the required stability to withstand a specific force. The function calculates the shear force in the shear joint, and the required minimum diameter of the pin.

Use this function to check whether a radial pin that was inserted for the connection of a shaft and a hub has the required stability. The function calculates the minimum diameter of the pin, the shear stress in the pin, the torsional stress and the tensioning pressure in the shaft, and the tensioning pressure in the hub.