 > Move+Rotate
> Move+Rotate 3-D Standard > Transform > Move  > Move+Rotate
> Move+Rotate
You use this function to move+rotate the active object simultaneously. The following functions are available:
|
|
Moves and rotates the current part by specifying the displacement vector and the rotation axis. |
|
|
Move+Rotate part, via fitting points Moves and rotates the current part by specifying "fitting point pairs". |
3-D Standard > Transform > Move  > Move+Rotate
> Move+Rotate 
The active part is moved and rotated in one step.
To move and rotate a part in one step, you can also use the ...via fitting points function. If you select this function, the transformation will be performed by specifying three fitting point pairs. The fitting points on the part are transformed to the drawing's corresponding fitting points.
![]() The function is not available for clonings.
The function is not available for clonings.
3-D Standard > Transform > Move  >... via fitting points
>... via fitting points 
You use this function to move and rotate the active part simultaneously.
To do this specify 3 fitting point pairs, one after the other. The fitting points on the part are transformed to the drawing's corresponding fitting points, with the part retaining its original dimensions.
Internally, the following steps are performed in this function, with each of these steps being graphically visualized as follows:
During fitting point specification in the model drawing, you can right-click to open a context menu with further point specification functions.
Use the Origin function to place the fitting point in the origin of the active coordinate system. Use the Step back function to select a new fitting point on the part.
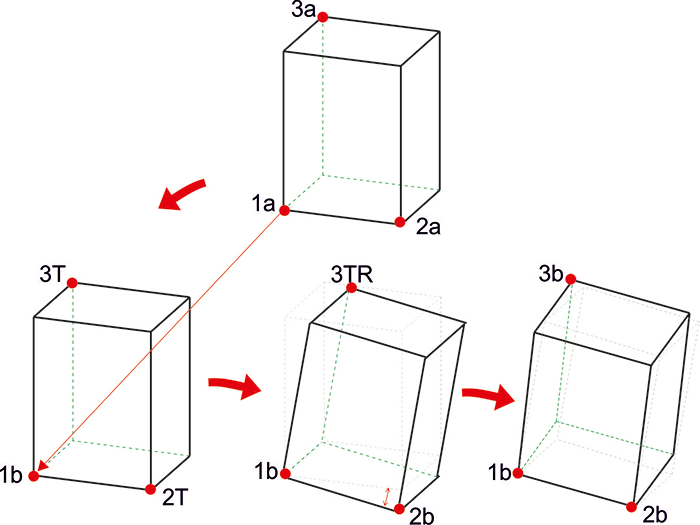
(1,1') determines the moving, (2,2') determines the rotation about the normal through 1', (3,3') determines the rotation about the rotation axis 1'2

|
© Copyright 1994-2018, ISD Software und Systeme GmbH |