Convert Point Clouds
There are several ways to call the converter:
Call from HiCAD
Point cloud > Tools > Conv... 
Drawing > Insert Part > Exp.  > Point cloud conversion
> Point cloud conversion 
To start the Point Cloud Converter directly from HiCAD, choose the Start point cloud conversion function - either directly via the Point cloud tab or via the menu Drawing > Insert Part > Exp.  > Point cloud conversion.
> Point cloud conversion.
|
|
|
After calling the function, the Point cloud conversion dialogue window will be displayed.
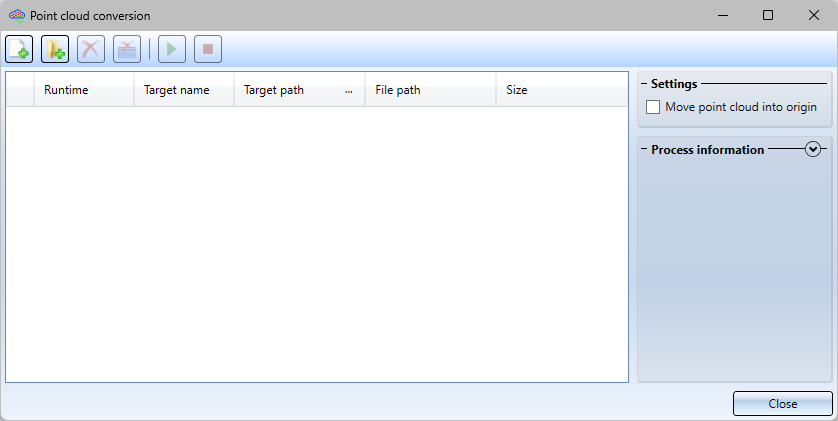
To select a file for conversion, click on the Add point cloud file  icon and then select the .E57 file to be converted. You can also add multiple files, which will then be converted one after the other. Add point cloud file
icon and then select the .E57 file to be converted. You can also add multiple files, which will then be converted one after the other. Add point cloud file  selects all .E57 files from the folder that are to be converted.
selects all .E57 files from the folder that are to be converted.
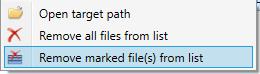
Click on the Remove all files from list  icon to remove all files from the list. To remove a single file or all selected files from the list, click on the Remove selected file(s) from list
icon to remove all files from the list. To remove a single file or all selected files from the list, click on the Remove selected file(s) from list  icon.
icon.
Click on the  icon to convert all files in the list. The
icon to convert all files in the list. The  icon next to it stops the conversion.
icon next to it stops the conversion.
If you right-click on a row, you have two options for deleting the file(s). You can also open the target path.
|
Column |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
Runtime |
Here it is shown since when the current conversion has been in progress. |
|
Target name |
The target name, i.e. the name of the generated project point cloud (.LSPROJ) cannot be changed. The name of the selected .E57 file is automatically used. |
|
Target path |
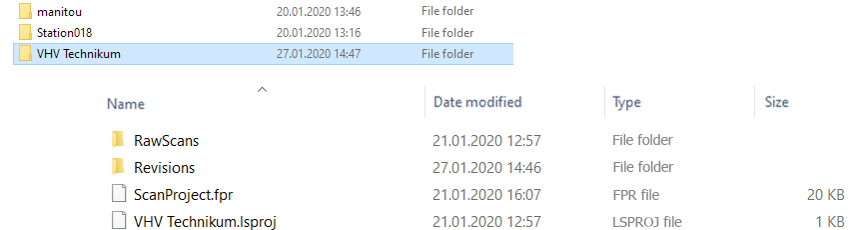
Target path is the path set in the HiCAD file filegrup.dat for the file group N. This can be a network path or a local path. The ISD-side default setting is the sub-folder point clouds of the HiCAD installation. During conversion, a subfolder with the name of the file to be converted is created in the target path. This folder then contains the project point cloud (.LSPROJ) created by the conversion, as well as further sub-folders, e.g.:
The target path can be opened with the corresponding function of the context menu. However, please note that the path cannot be changed here. |
|
File path |
Shows the path where the .E57 file to be converted is located. |
|
Move point cloud info origin |
This function can be used to place the point cloud into the origin (0, 0, 0) of the coordinate system. |
|
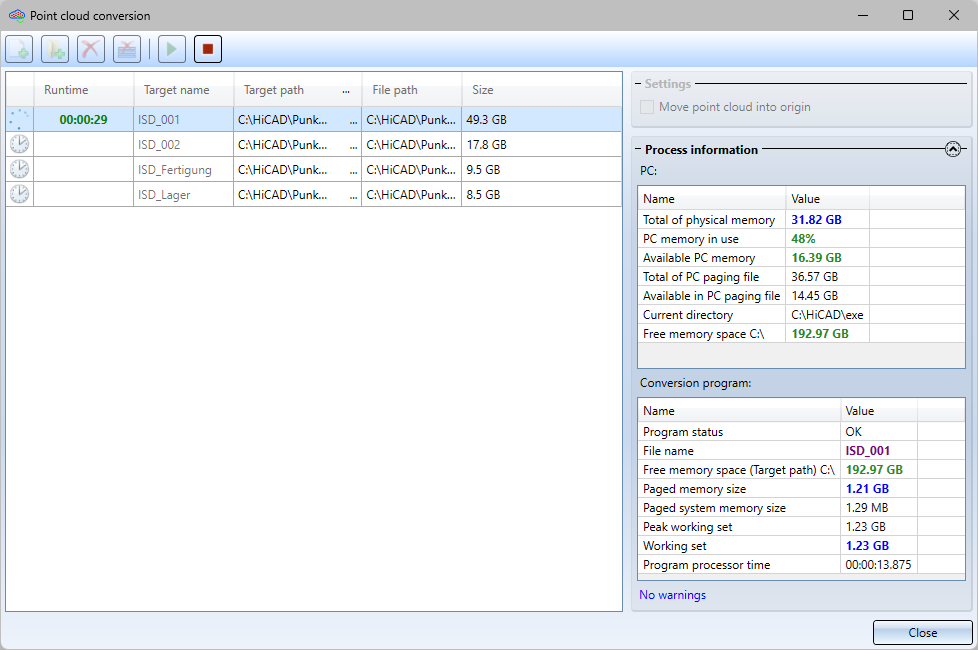
Process information |
Here you can see how busy your PC is when it is being converted. You can also see how much of your complete working memory is available. You will also see information about the swap file, the directory and the free memory space.
|
|
Process information |
Here you will find the status and the file name first. Next, the free memory space and the allocated program memory are listed. Then you will find the amount of data swapped out, as well as the maximum amount of memory used by the program and the amount of memory currently used. Finally, you will find the processor time required by the program.
|
|
Warnings |
A warning is displayed here if problems occur. For example: Very high memory utilisation! If there is not enough memory available, processes in HiCAD are executed much more slowly, which can result in very long waiting times. In extreme cases, the program may crash. |
You start the conversion by clicking the Convert button. The files are then converted one after the other. If an error occurs during the conversion or if a converted file already exists under the name, the corresponding row will be marked with the  symbol. If you point with the cursor at the symbol, a corresponding error message is displayed. The conversion will be cancelled, for example, if the points are so far away from the origin that display errors occur. Then start the conversion again with the option Move point cloud into origin or change the position of the cloud in the e57 file.
symbol. If you point with the cursor at the symbol, a corresponding error message is displayed. The conversion will be cancelled, for example, if the points are so far away from the origin that display errors occur. Then start the conversion again with the option Move point cloud into origin or change the position of the cloud in the e57 file.
To cancel a conversion in progress, right-click on the corresponding row and choose Cancel, or click on Cancel in the dialogue window.
If you close the window while the conversion is in progress, the conversion will be aborted.
External call
The point cloud converter can also be started outside HiCAD. To do so, run the file PointCloudConverter.exe in the EXE directory of the HiCAD installation. The operation is the same as when calling the converted from HICAD.
Call via Command Prompt
The converter can also be started by command line call at the command prompt by running the file PointCloudConverterConsole.exe with the required parameters.
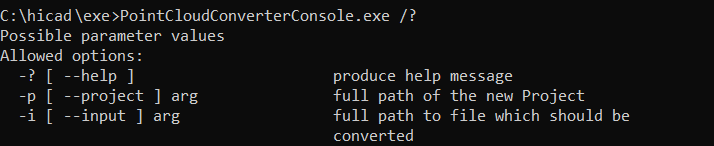
The supported parameters are:
| Parameter | Effect |
|---|---|
-?
oder --help |
Displays a short summary of the supported parameters. |
-p arg
oder --project arg |
Specifies the target of the conversion. arg must be a path. If the path contains spaces, it must be enclosed in quotation marks. The last element of the path is used as the file name of the Example: The parameter |
-i arg
oder --input arg |
Specifies the path and file name of the .E57 file to be converted. If the path contains spaces, it must be enclosed in quotation marks. |
No output is made during the conversion. If the conversion was successful, the message
conversion of <file> has been completed succesfully
is displayed at the end. If the conversion could not be carried out, the message
conversion of <file> has failed
is output. To cancel a conversion prematurely, press the key combination Ctrl+C.
A possible use case for the conversion via command line would be the automatic conversion of .E57 files via a batch file.
The basis for this could be a batch file with the following content
@echo off
for %%i in (C:\Punktwolken\*.e57) do C:\HiCAD\exe\PointCloudConverterConsole.exe -i "%%i" -p "C:\HiCAD\punktwolken\%%~ni\%%~ni"
This searches for .E57 files in the folder C:\Point clouds and calls the converter for each file found. The converted data is created in the folder C:\HiCAD\point clouds\<base name>, where base name is the name of the .E57 file without the file extension. If, for example, there is a file Station018.e57 in C:\Punktwolken, this data is saved in the folder C:\HiCAD\punktwolken\Station018.
As the converter aborts if there is already a point cloud project at the destination, .E57 files that have already been converted are not converted again even if the script is called up again.