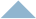
Motion Simulation: Motors with Reference Part
- Part with translation motor, reference part with translation motor
- Part with rotation motor, reference part with translation motor
Part with translation motor + reference part, reference part with translation motor
For this simulation you use the example of the motion simulation with two time intervals. Delete the delete motors 1 and 3.
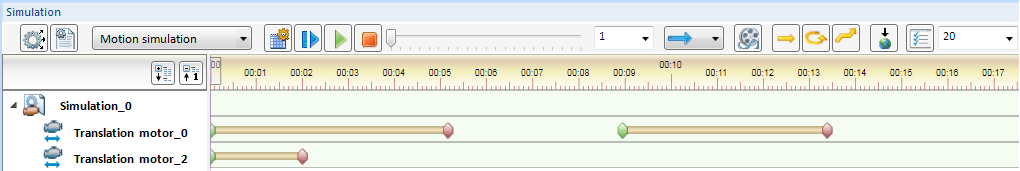
Now, Box2 is to be used for Translation motor_0. Proceed as follows:
- Double-click Translation motor_0
- Activate the checkbox.
- Click the
 symbol and identify Box2.
symbol and identify Box2. - Close the window with OK.
- Set the collision check.
- Calculate
 the simulation.
the simulation.
Video of the simulation
Part with rotation motor and reference part, reference part with translation motor
For this simulation you use the following example:
For Box1 you want to define a rotation motor, and use Box2 as the reference part. For Box2 you want to define a translation motor.

First activate the assembly. Then proceed as follows:
- Select New simulation
 .
. - Select Translation motor
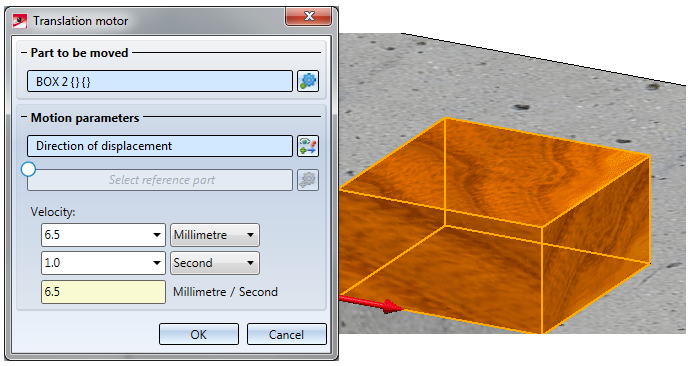
 (Part to be moved: Box2; Direction: lower edge of box (a); Velocity: 6.5 mm/sec.)
(Part to be moved: Box2; Direction: lower edge of box (a); Velocity: 6.5 mm/sec.)
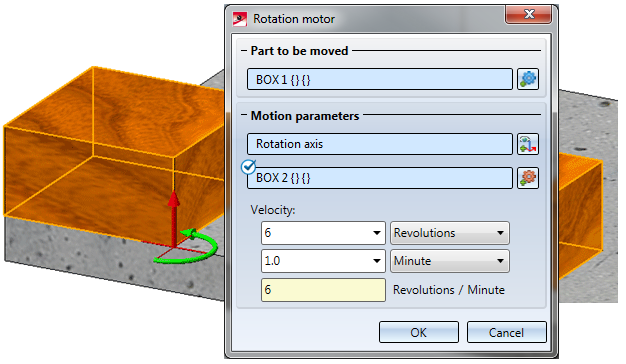
- Now select Rotation motor
 (Part to be moved: Box1; Rotation axis: right front edge; Velocity: 6 revolutions per minute; Reference part: Box2)
(Part to be moved: Box1; Rotation axis: right front edge; Velocity: 6 revolutions per minute; Reference part: Box2)
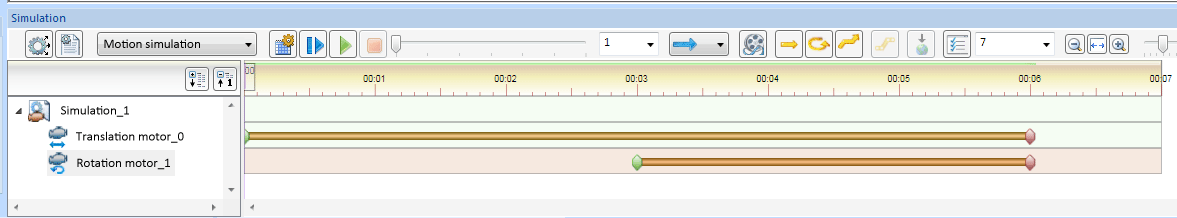
- Define the time intervals:
- Max. simulation time
- Translation motor: 0 - 6 s
- Rotation motor: 3 - 6 s
- Calculate
 the simulation.
the simulation.
Video of the simulation
In this example, the Reference part option has the following effect:
According to the time interval, the rotation motor will only start after 3 seconds. As the rotation motor uses Box2 as the reference part, and the translation motor defined for the reference part starts after 0 seconds, (i.e. immediately), Box1, too, will be displaced immediately, and rotated only after 3 seconds.
If you changed the rotation speed for the rotation motor to 0, or moved the Start switch to the end of the simulation, Box1 would simply adopt the displacement of Box2 and move in an identical way.

The 'Simulation' Docking Window' (3-D) • Simulation: Examples (3-D)