Define Central Projection
- Automatic central projection
- Redefine central projection
- Central projection, viewer distance
- Central projection, angle of vision
- Central projection, line of vision
![]() Important:
Important:
- Parts may be hidden in the central projection if the viewpoint calculated from the specified parameters is too close to the object.
- When working in the central projection, not all point options may be available, e.g. the point option (Z) Centre. Therefore, a creation and processing of 3-D models in the central projection is not recommended.
Automatic central projection
Views > Projections >Standard AXO > Automatic central projection 
HiCAD determines central projection automatically here, choosing the following data:
- The line of vision results from the current projection.
- The spatial centre lies in the centre point of the view.
- The angle of vision and the viewer distance will be calculated automatically.
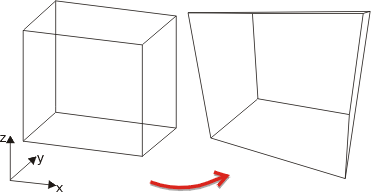
Redefine central projection
Views > Projections >Standard AXO > Redefine central projection 
You use this function to define a central projection by entering all required parameters.
- Define the spatial centre by means of point determination. Right-click to apply the previous spatial centre and press the middle mouse button to apply the midpoint of the drawing.
- Specify the viewpoint. The line of vision is now defined by means of the line viewpoint-spatial centre.
- Enter the viewer distance. If you want a parallel projection to be created, choose 0. The viewpoint will then lie at infinity.
- Specify a point on the horizon. This point determines the position of the x-axis of the screen plane.
- Enter the angle of vision.
Central projection, viewer distance
Views > Projections >Standard AXO > Central projection, viewer distance 
You use this function to define a central projection by specifying the spatial centre and the viewer distance. The line of vision of the current projection will be retained.
Once you have selected the function, HiCAD marks the current spatial centre.
- Define the spatial centre by means of point determination. Right-click to apply the previous spatial centre and press the middle mouse button to apply the midpoint of the drawing.
- Enter the viewer distance.
Central projection, angle of vision
Views > Projections >Standard AXO > Central projection, angle of vision 
You use this function to define a central projection by specifying the spatial centre and the angle of vision as well as choosing the viewpoint. As all perpendiculars to the active xy-plane remain parallel, this function enables one-point and two-point projections to be created.
- Define the spatial centre by means of point determination. Right-click to apply the previous spatial centre and press the middle mouse button to apply the midpoint of the drawing.
- Specify the angle of vision.
- HiCAD fades in the axis viewpoint-spatial centre and the angle of vision α instead of the crosshairs at the cursor. You can then use the cursor to choose any viewpoint.
Central projection, line of vision
Views > Projections >Standard AXO > Central projection, line of vision 
You use this function to create one-point or two-point projections.
- Define the spatial centre by means of point specification. Right-click to apply the previous spatial centre and press the middle mouse button to apply the midpoint of the drawing.
- Enter the viewer
distance.
If you want a parallel projection to be created, choose 0. The viewpoint will then lie at infinity. - Specify the angle of the line of vision with regard to the x-axis.
The horizon results from the xy-plane of the active coordinate system. You can change the position of the xy-plane by defining a local coordinate system.

Axonometric and Isometric Projection (3-D) • Projection Methods (3-D) • Central projection (3-D)