Transform + Clone Part
Transforming a part means to assign it specifically to other parts of the drawing so as to guarantee the technical function (e.g. shaft-cog wheel, valve flange-pipe flange). In constructive tasks, this is generally done via the surfaces of the parts and/or via marked lines or points, e.g. symmetry lines, midpoints, centroids.
Transforming a part in 3-D space may require the following elementary operations, in accordance with the 6 degrees of freedom:
- Move in x-, y- or z-direction or
- Rotate about the x-, y- or z-axis.
In addition, scaling of a part in x-, y- and/or z-direction may be required.
Three 3-D fitting point pairs are generally required for defining the six degrees of freedom, e.g. when moving parts.
|
|
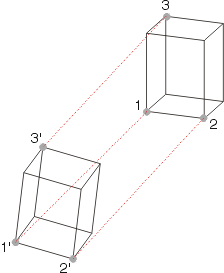
The figure shows the movement of a cuboid from the original position resulting from the specification of the three fitting point pairs (1,1'), (2,2') and (3,3'), i.e. the cuboid is rotated and moved. 1, 2 and 3 are the fitting points of the original position, while 1', 2' and 3' the corresponding fitting points in the drawing, i.e. the new positions of points 1, 2 and 3. |
You can copy parts that you require frequently in the drawing. These copies which are the result of a transformation from the original are called clones in HiCAD.
 Important:
Important:
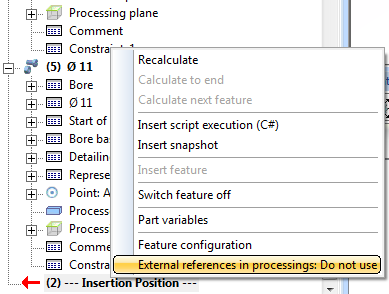
When cloning parts with external references (e.g. processings referring to elements of different bodies), the external references will only be taken over if the part to which the reference is made will also be copied.
If a part with external reference is copied without the corresponding reference part, the option will be set to External references in processings: Do not use.
If you want the external references of the processings to be preserved, you can switch the option to Use again afterwards. The position of the part will then change accordingly after recalculation.
Generally, you can also select the Body setting for individual parameters here, i.e. the parameter will behave as set for the part. During copying, the settings of the option will also be set to Do not use.