
In 2-D
Starting from the current cursor position, HiCAD determines the closest tangential osculation point of a line with a circle, an ellipse or an arc. The line here is defined by means of the current cursor position and the last point.
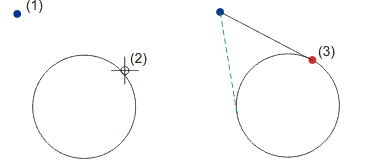
(1) Last point, (2) Cursor position, (3) Found point
In 3-D
Here, you determine the osculation point from the current 3-D point to an analytical 3-D part. The following options can occur:
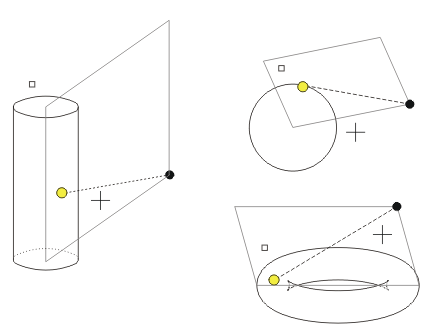
![]() = Current point,
= Current point, ![]() = Osculation point,
= Osculation point, ![]() = Cursor position,
= Cursor position,
![]() = Additional point
= Additional point
Osculation point from the current 3-D point to an analytical 3-D part
Here, you determine the osculation point from the current 3-D point to an analytical 3-D part. In contrast to option T, the plane in which you want the new point to lie is determined by identifying two edges.
This option can only be called via the keyboard.
With this option you determine the intersection of two tangents. HiCAD will request you to identify two graphical elements you require. The tangent will be defined by the end point of the graphical element lying closer to the cursor position. The new point is the intersection of both tangents.
If the same graphical element is identified twice, for instance as arc, the intersection of tangents will be defined on both end points of the graphical element.
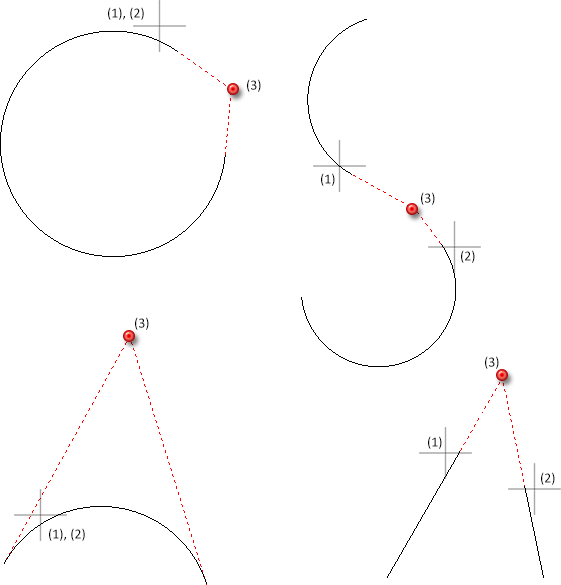
(1), (2) - selected graphical elements (here planar sketch), (3) identified point
 If the calculation of the point is not possible, for instance because the same graphical element has been selected, a respective error message will occur.
If the calculation of the point is not possible, for instance because the same graphical element has been selected, a respective error message will occur.

|
© Copyright 1994-2018, ISD Software und Systeme GmbH |