 > Surface, Further... > Optimise part
> Surface, Further... > Optimise part 
3-D Standard > Tools > Surface  > Surface, Further... > Optimise part
> Surface, Further... > Optimise part 
The functions of the Polyhedral model window enable you to approximate, optimise and triangulate 3-D parts.
You use the options in the top row to define the objects to which you want the operations of the bottom row to be applied:
|
|
Active part The operation is only applied to the active part. This is the default setting. |
|
|
Entire drawing The operation is applied to all parts of the drawing. |
![]() Approximate
Approximate
Approximates analytically created surfaces by means of polyhedrons.
You define the number of polygon points for 3-D quadrants via
Drawing > Properties > Attr. > Surface approximation.
> Surface approximation.
Alternatively, you can also select Properties > Surface approximation in the context menu of the drawing to define the number.
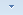
(1) Analytical, number of polyhedral points = 0 (2) Polyhedral model, number of polyhedral points = 6 (3) Polyhedral model, number of polyhedral points = 2
![]() Triangulate
Triangulate
Triangulates surfaces that are bounded by polygons with more than three vertices.
These surfaces are divided into triangles. Analytical parts with curved surfaces need to be approximated before triangulation.
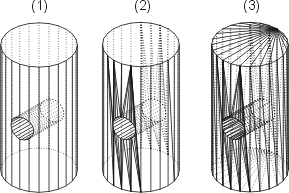
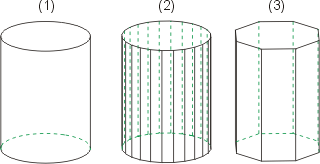
(1) Original part with convex surfaces (2) Without triangulation of the convex surfaces (3) With triangulation of the convex surfaces
![]() Optimise
Optimise
Reduces memory requirements by unioning (divided) edges and surfaces.
On completion of the optimisation, the number of unioned edges and surfaces (facets) is displayed. For parts with many edges and surfaces, this function may result in more free memory space after part operations, corrections and/or processing.
You can also use this function to merge divided or triangulated surfaces.
Free-form surfaces that can be displayed as analytical surfaces are automatically converted during Optimisation. If you do not want this to happen, you need to change the following entry in the system file SPLINE.DAT from 1 to 0:
Do you want FFS to be converted, if possible, to analytical surfaces once they have been created? (Can be useful for sheet parts)
0: FFS remain FFS
1: FFS are converted, if possible, to analytical surfaces once they have been created.

Part Tools (3-D) • Model and Process Parts (3-D)
|
© Copyright 1994-2018, ISD Software und Systeme GmbH |