 > Divide, Number
> Divide, Number 
Sketch > Process > Trim  > Divide, Number
> Divide, Number 
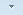
Use this function to divide lines of a sketch by specifying the number of segments. In the process you can specify whether the resulting segments are to be converted into lines or not.
After calling the function, enter the number of desired segments first. If you want to convert the curve segments into straight lines, activate the Convert curves into straight lines checkbox. The checkbox has no effect on straight lines.
When you move the cursor over a line in the drawing, it will be highlighted (magenta, Special colour "Marking 1") and the division points will be shown in the form of symbols. Click to select a line and highlight it (red, Special colour "Marking 5"). If an already selected line is selected again, it will be excluded from the selection, and its highlighting will be removed.
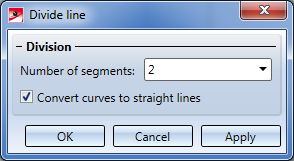
Example: (1) Original sketch, (2) Preview, (3) Marking after selection - 3 segments, no conversion to lines
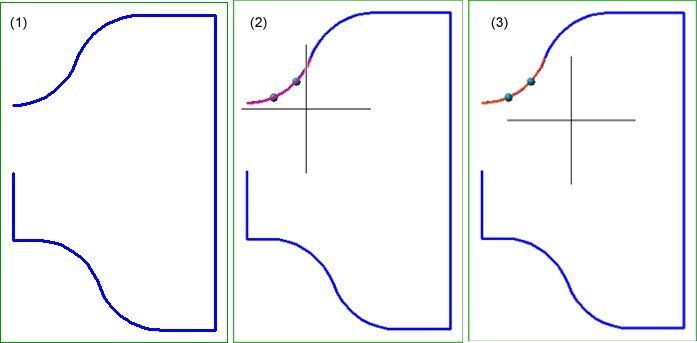
Conversion to lines: Example
If you right-click during the selection process, a context menu with further options will be displayed:
|
|
Connected lines or edges* Use this function to select all lines or edges that are connected to the next identified edge in one step. The lines and edges will be selected up to a point where the continuation is no longer unambiguous.
|
|
|
Connected lines (only straight lines) Divides all straight lines of a polyline. Curves will not be considered. |
|
|
Connected lines (only curves) Divides all curves of a polyline. Straight lines will not be considered. |
|
|
Tangentially connected lines or edges* Same as above, but for tangentially connected lines.
|
|
|
Lines in rectangle (CTRL+LMB)* Use this function to select lines by means of a selection rectangle. Please note that only lines of the active part will be considered. If the rectangle is drawn from the top left to the bottom right, all lines which are completely located within the rectangle will be selected. If the rectangle is drawn from the top right to the bottom left, lines only portions of which are located within the rectangle (i.e. intersect with the rectangle) will be selected as well. The selected lines will be highlighted in a different colour. You can also call the function via the keyboard. Proceed as follows:
If you draw a rectangle around already selected lines / edges, these will not be deselected!
Selection of lines via rectangle |
|
|
Step back If you want to undo one or several steps of the process in order to make corrections, select this option (if required, several times). |
|
|
Cancel (ESC) Cancels the edge selection. |
Important note on the selection functions:
Normally, already selected lines and edges will be de-selected if you click them again.
For the above functions marked with an asterisk *, however, the following applies: If you click lines or edges that have already been selected or if already selected lines are located in a selection, they will not be removed from the selection!
If you want the lines highlighted in red to be divided as shown in the preview, click OK or Apply in the dialogue window. After OK the window will be closed after the division, after Apply the window will remain open, enabling you to apply further divisions if desired. If you choose Cancel, no division of the selected lines will take place.
If you middle-click in the drawing while the dialogue window is displayed, the following will happen:
HCM constraints
If the Enter constraints checkbox has been activated in the HCM settings Sketch > HCM > Tools  > Settings), the following constraints will be assigned to the elements resulting from the line division:
> Settings), the following constraints will be assigned to the elements resulting from the line division:
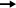 Coincidence
Coincidence 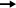 Same radius + Coincidence of centre points
Same radius + Coincidence of centre points 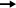 Same radius + Coincidence of centre points
Same radius + Coincidence of centre points 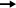 Tangential
Tangential
If any HCM constraints had already been assigned to the divided line when you apply the function to it, the following will happen:
HCM constraints can also be referred to centre points of circles or ellipses. If you divide a circle or an ellipse the HCM constraints of which refer to its respective centre point, one segment ("preferred segment", which will also keep the internal feature name) will keep these HCM constraints at its mid point; the mid points of the other segments, in contrast, will obtain "Coincidence" constraints referring to the mid point of the "preferred" segment.

Sketch Functions (3-D) • Process Sketch (3-D)
|
© Copyright 1994-2018, ISD Software und Systeme GmbH |