![]()
HiCAD finds the intersection point of two lines that lies closest to the cursor position.
The option identifies the theoretical intersection point lying on the extension of two lines.
You cannot use this option to detect the intersection point of two conic sections or a circle with a conic section. Use option S for this.
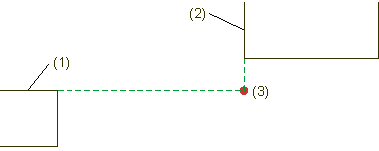
(1) First line, (2) Second line, (3) Theoretical intersection point
![]()
You define the intersection point of a 3-D edge with a surface here.
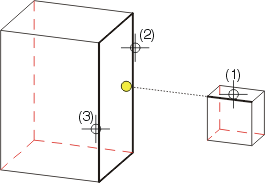
(1) Edge, (2) First edge for surface, (3) Second edge
for surface, ![]() = Found point
= Found point
![]()
Intersection point 2-D/3-D lines .png)
You use this option to define the intersection point of 2-D and 3-D lines.
Identify:
The point found is the intersection point of the two edges.
The point found is the intersection point of the two graphical elements. Next, you need to enter the z-coordinate of this point.
The point found is the projection of the 2-D intersection point of the two elements onto the 3-D edge.

(1) Edge, (2) First edge for surface, (3) Second edge
for surface, ![]() = found point
= found point
Related Topics
Version 1702 - HiCAD Basics | Date: 9/2012 | © Copyright 2012, ISD Software und Systeme GmbH